Notes on Recent Talks about Autonomous Intelligence by Yann LeCun
Published:
This note includes insights from Yann LeCun, often referred to as the father of deep learning. In his talk, he discussed the limitations of current machine learning methods and self-supervised learning methods. He emphasized the need for objective-driven AI and introduced the concept of a modular cognitive architecture, also known as the world model. Additionally, he introduced the Joint-Embedding Predictive Architecture (JEPA), a new approach in the field.
Introduction
The limitation of machine learning
- Supervised learning requires many label data
- Reinforcement learning requires many trials
- Self-supervised learning only works well with text/other discrete modalities
Compare with human and animals:
- learn new tasks quickly
- can reason and plan
- have common sense
- their behavior is objective driven
Self-supervised Learning (SSL)
What is SSL?
- Learning to fill in the blanks
- Example in NLP domain:
- Sentence is masked/corrupted:
- The sun was shining brightly in the clear blue sky. → The sun was shining __ in the clear blue __ .
- Sentence is masked/corrupted:
- In the process of learning to fill in the blank, the model learned the representation of natural language
Why is SSL effective in text but not as much in images?
- Natural language is finite, finite amount of vocabulary
- Natural language is discrete
Generative AI and Auto-Regressive LLM
Autoregressive Generative Architectures
- Predict next token based on previous tokens
- Tokens can represent words, image patches, …
The limitations of Autoregressive LLM
- Hallucinations
- Logical errors and inconsistency
- Limited reasoning and planning
- LLM have limited knowledge of underlying reality, as they have no common sense and can’t plan their answer
Compare with human and animals:
- Understand how the world works
- Can predict consequences of their actions
- Can perform chain of reasoning with unlimited number of steps
- Can plan complex tasks by decomposing into sequences of subtasks
Autoregressive are doomed
\[P(correct) = (1-e)^n\]where $e$ is probability of wrong tokens produced.
- This diverges exponentially
- It’s not fixable without major redesign
Three Challenges for AI & ML in the future
- Learning representations and predictive models of the world
- Learning to represent the world in a non task-specific way
- Learning predictive models for planning and control
- Learning to reason
- Making reasoning and planning as energy minimization
- Learning to plan complex actions to satisfy objectives
- Learning hierarchical representations of action plans
Objective-Driven AI
Modular Cognitive Architecture
An architecture of different modules interact with each other
- Perception module:
- Computes representation of the state of the world from perception (possibly combined with memory)
- World model module:
- Predict the outcomes of series of actions given by the actor
- Actor module:
- Imagine a series of actions and feed to the world model
- Cost module:
- Evaluate the outcomes from the world model, measuring the quality of the outcomes
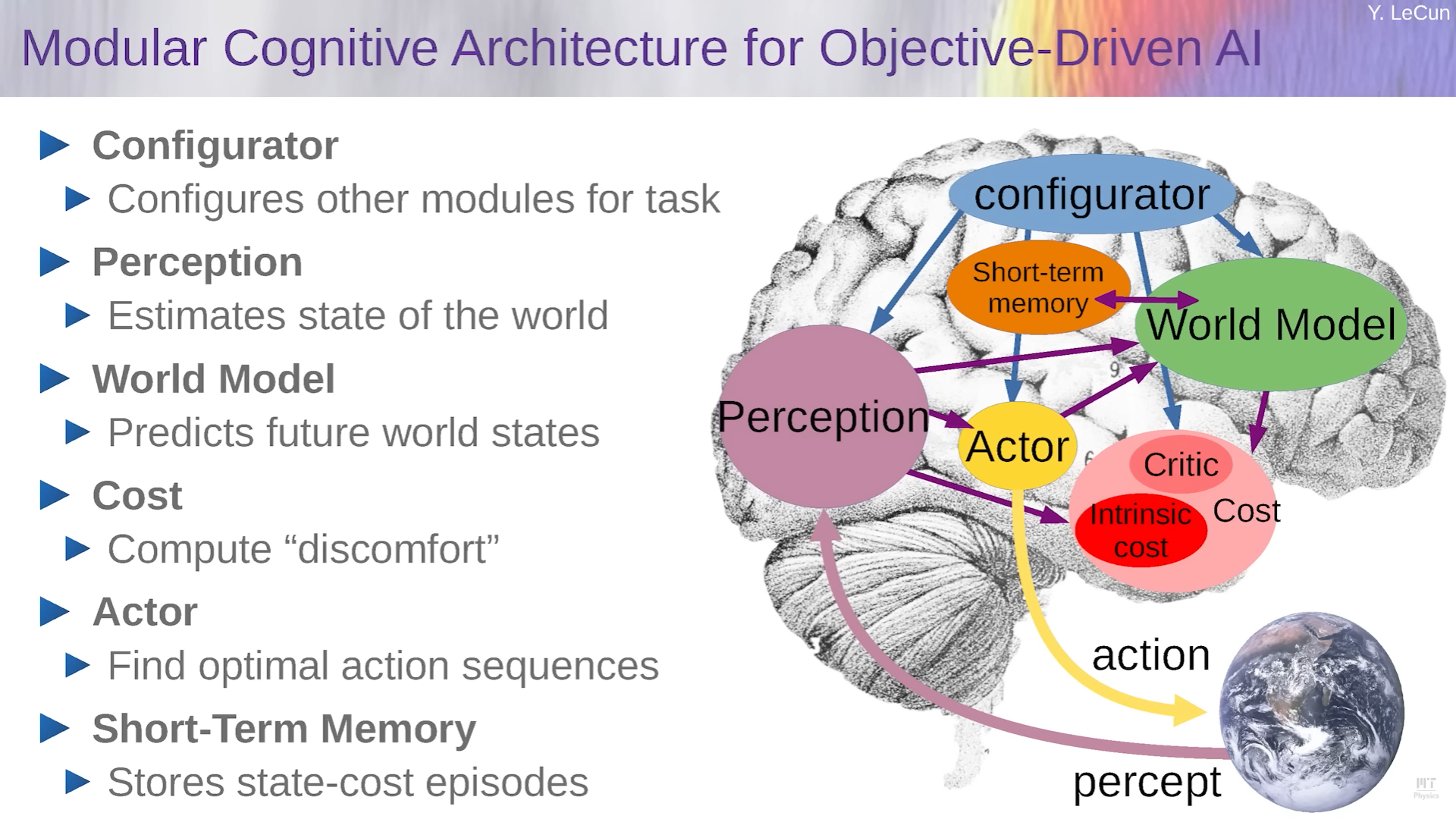
Perception-Action system
The purpose of the agent is to figure a sequences of actions that minimizes the cost during inference time. Therefore, inference is also an optimization process.
- Task objective: Measures divergence to goal
- Guardrail objective: Ensure trustworthy AI
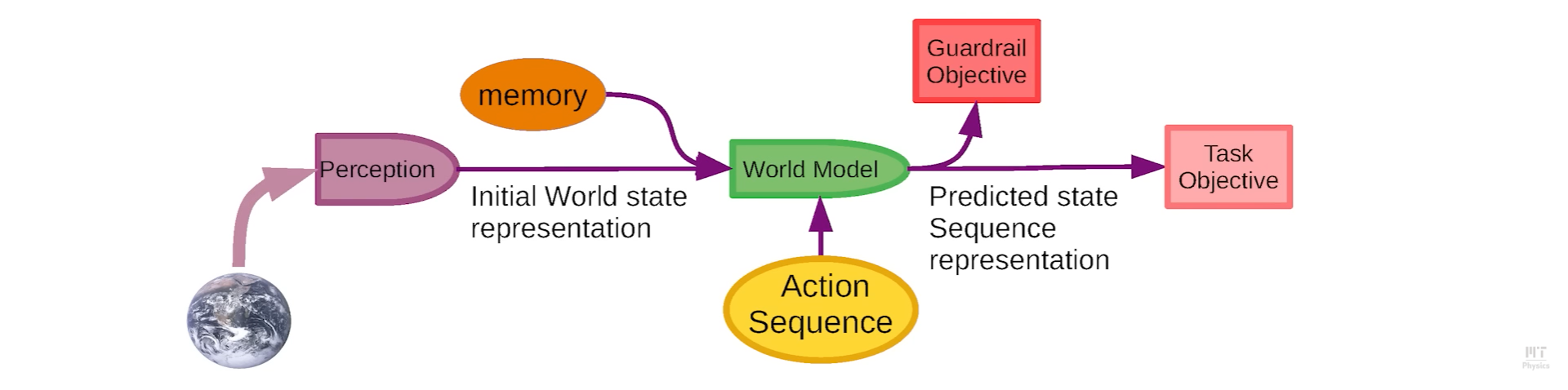
Perception-Planning-Action system
- think of this as multi-step or recurrent world model
- Same world model applied at multiple time steps with guardrail costs applied to every timestep.
- Similar idea with Model Predictive Control (MPC)
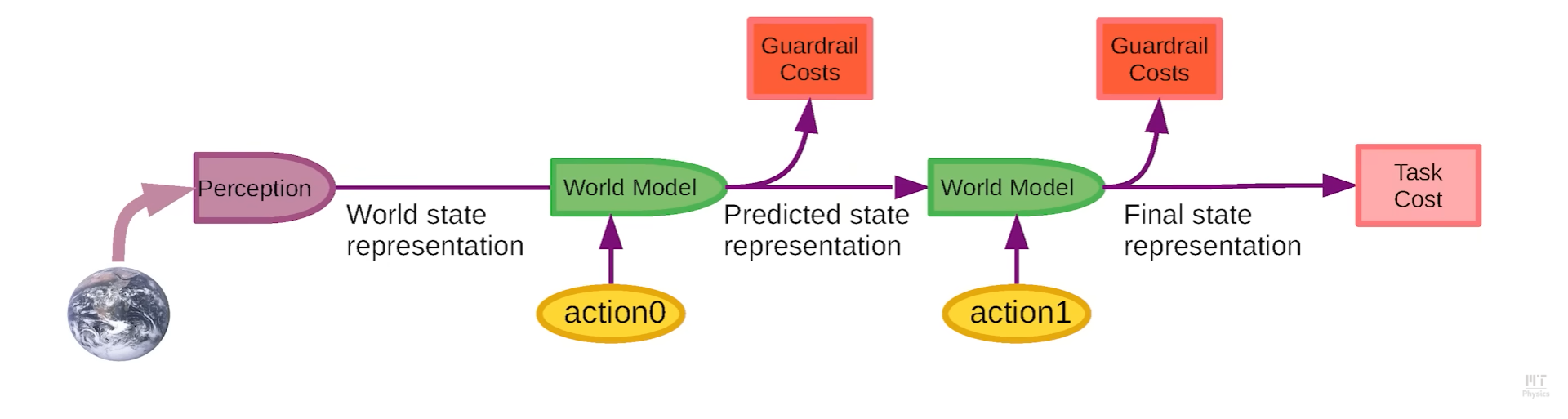
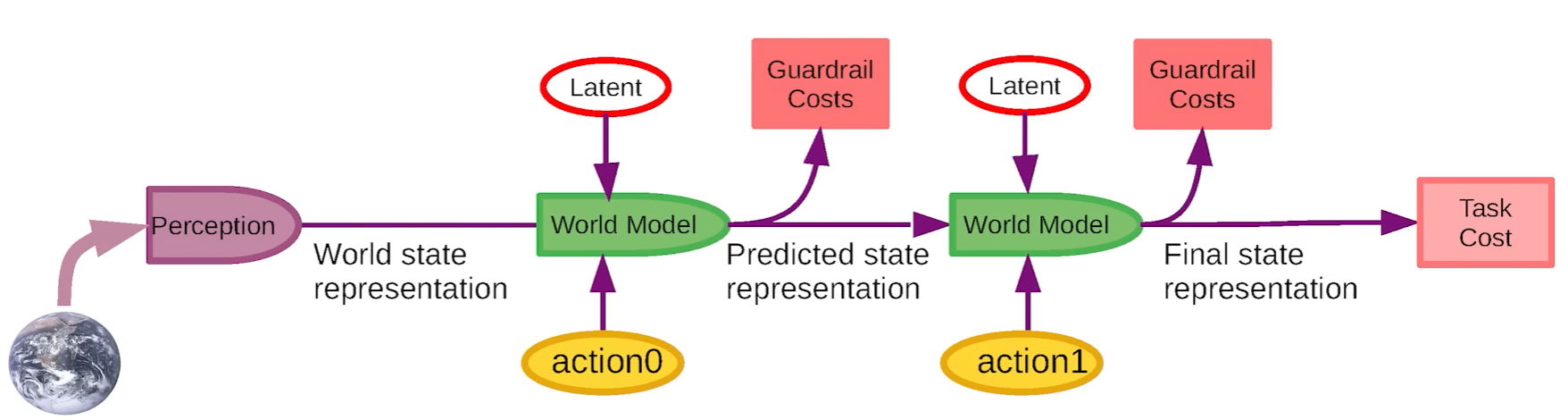
Non-Deterministic World Model
- The world is not deterministic, therefore we need to introduce latent variables to help capture the diversity
- So it can be multiple predictions for a single action
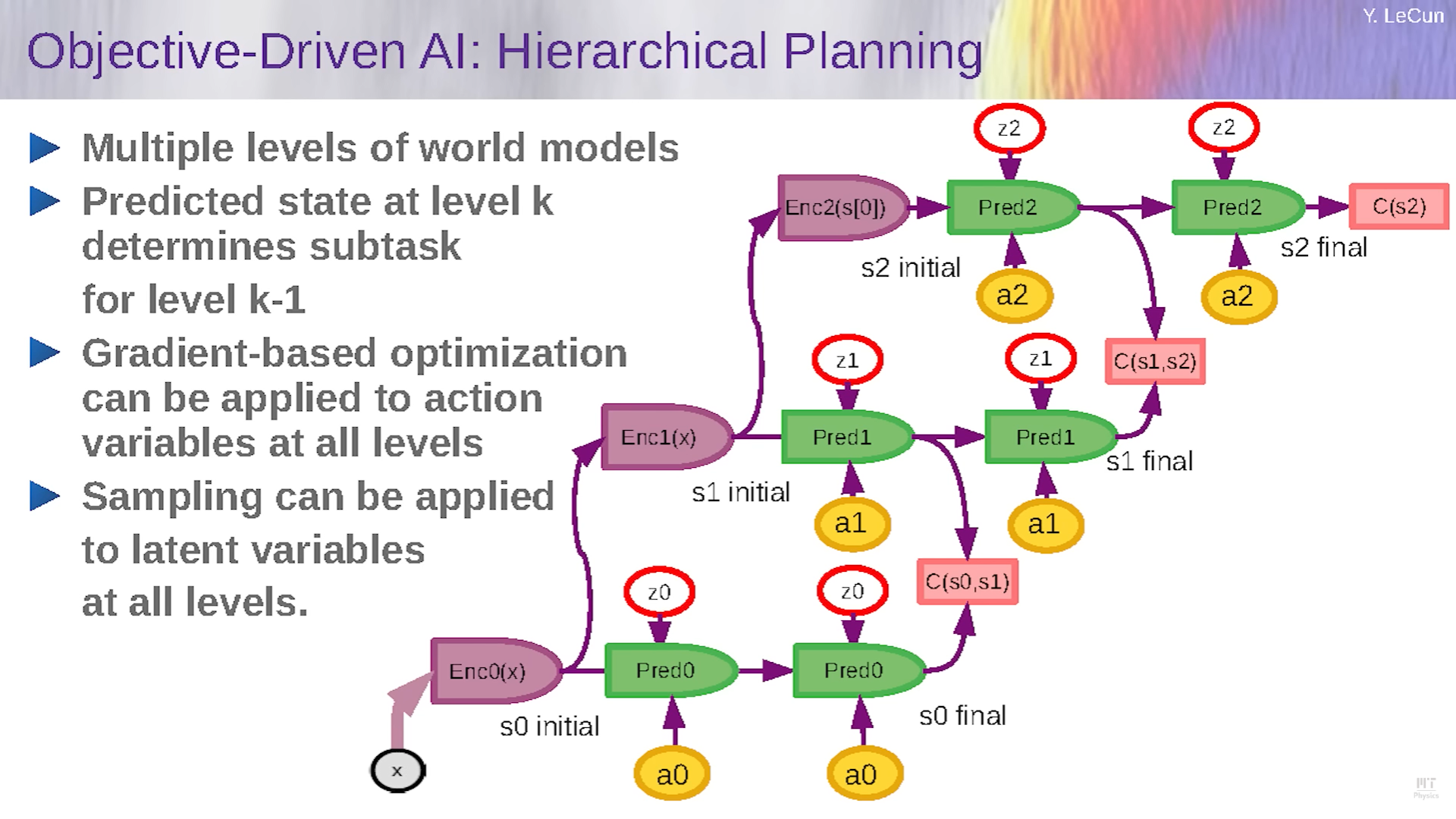
Hierarchical Planning
- We require a system capable of learning diverse levels of representations of the world’s state, enabling it to effectively decompose complex tasks, without explicitly designing the hierarchy
- Low-level representations only predict in the short term
- Too much details
- Prediction is hard
- High-level representations predicts in the longer term
- Less details
- Prediction is easier
Outlook for Objective Driven AI System
- If we had a system that was able to:
- Receive a query
- Conduct planning in the abstract representation space
- Then translate the representation into fluent text using autoregressive decoder, then
- If we have such system:
- We could have a AI model that is factual, fluent, non-toxic, etc.
- No need for RLHF or fine-tuning, because the model is constrained by the guardrail cost modules
Building & Training the World Model
Things that are easy for humans are difficult for AI and vice versa, we are missing something big!
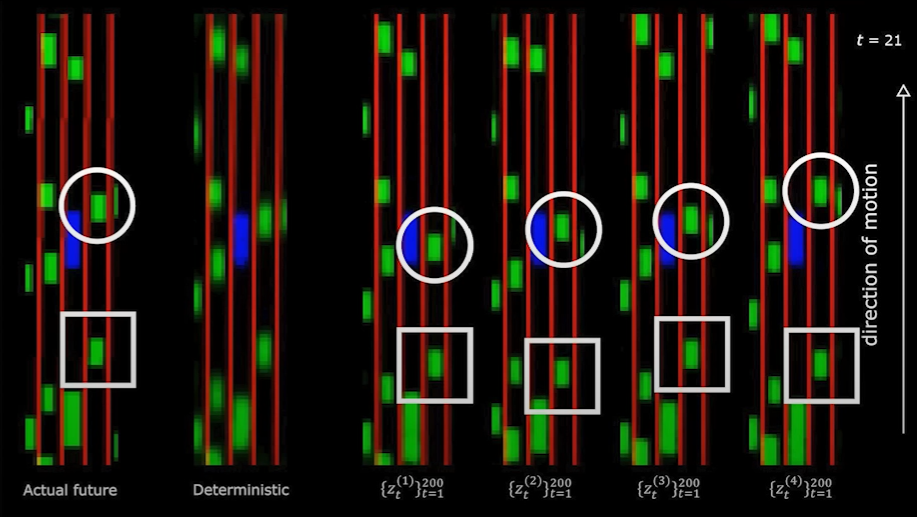
- Using SSL in the case of video prediction:
The predicted video frame is blurry, because the system is trained to make one prediction, which is an average of all the possible futures
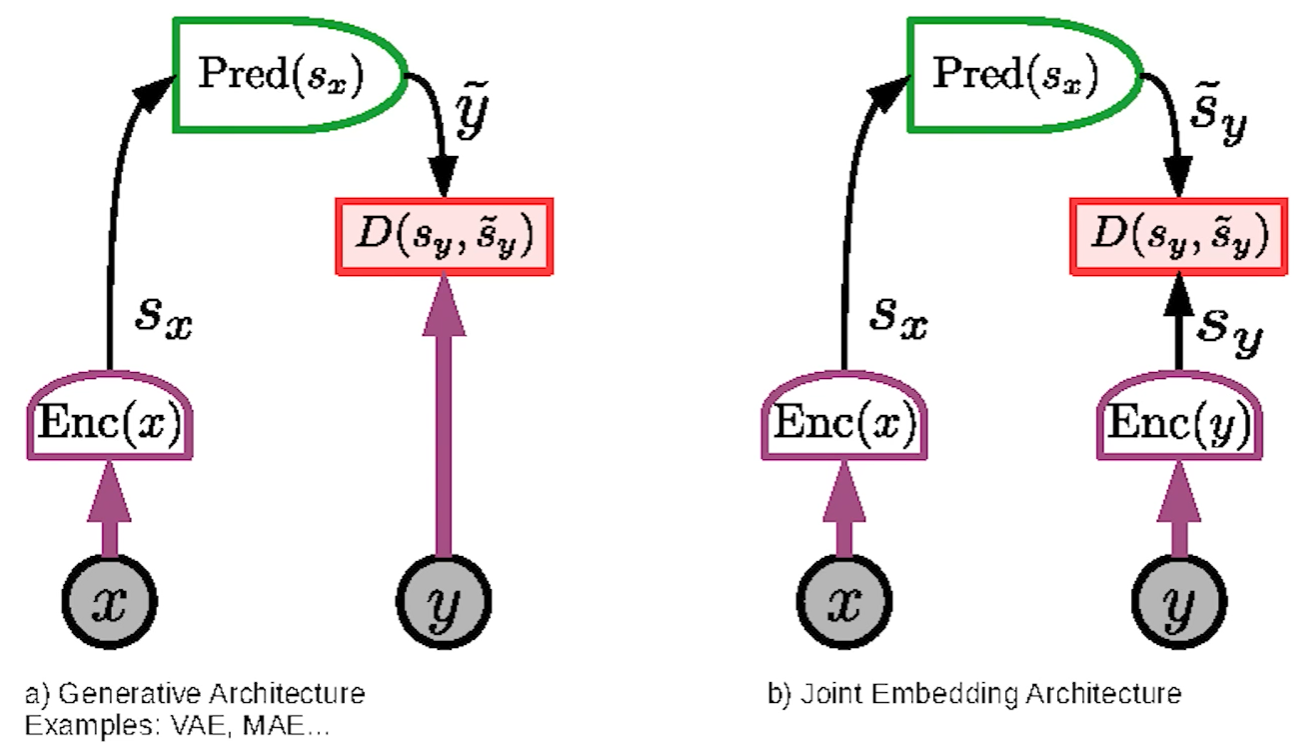
Joint Embedding
- Generative method:
- Encode input $x$ to get representation $S_x$ to predict variable $\tilde y$, then measure the divergence between ground true $y$ and predicted $y$
- Joint Embedding method:
- Encode input $x$ to get representation $S_x$, then predict representation $\tilde S_y$, then measure the divergence between $S_y$ and $\tilde S_y$
- Encoder $y$ has invariant properties:
- Map multiple $y$ into same $S_{y}$, therefore if $y$ is hard to predict, the encoder can eliminate the noisy information, only focus on the details relevant to the task
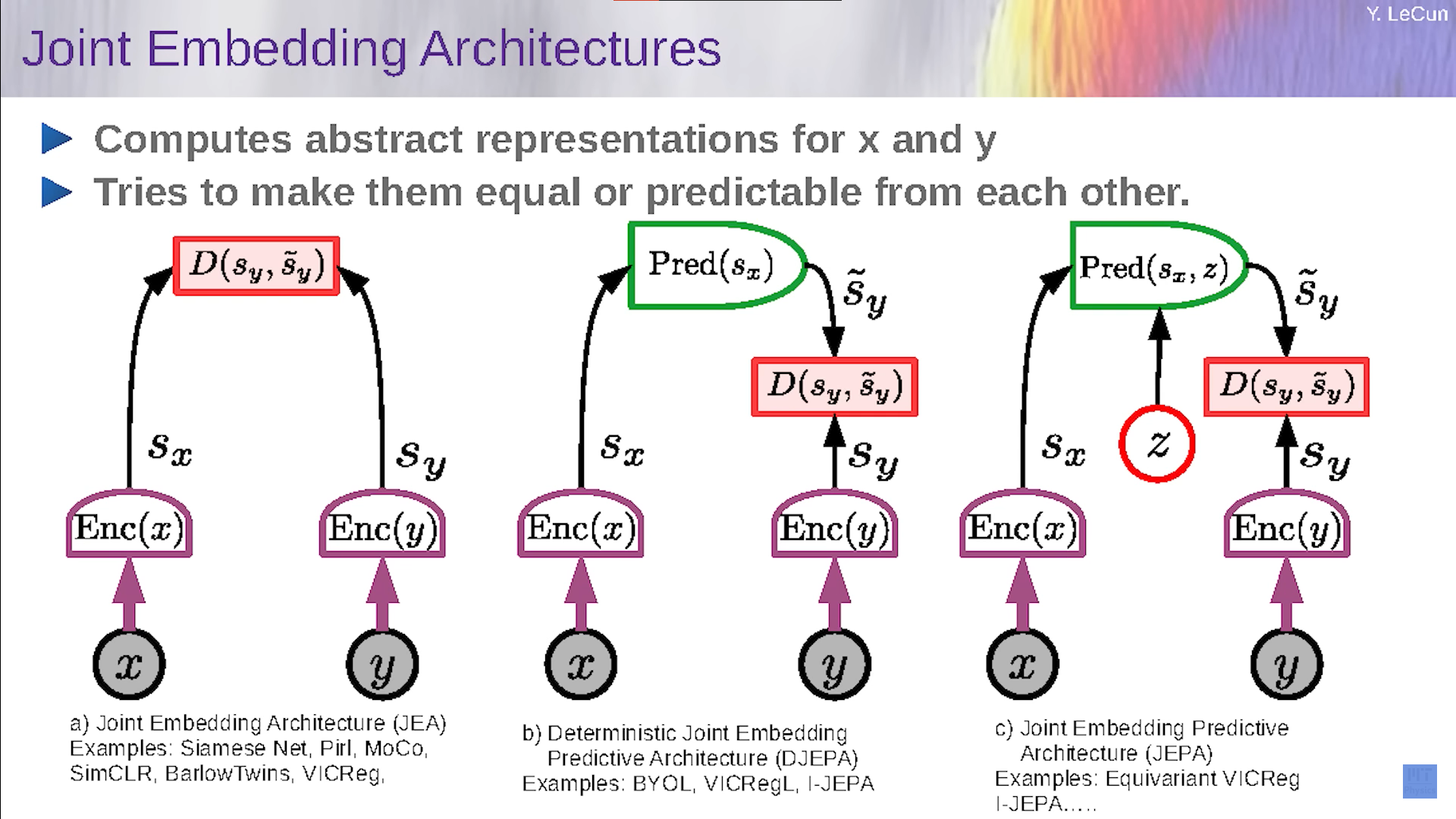
Joint Embedding Architectures Variants
- left: without predictor
- middle: with predictor
- right: with latent variable
- To train these variants, it might collapse
- Because we want the representations of $x$ and $y$, that is $S_x$ and $S_y$ to be identical
- No matter what the input $x$ and $y$ are, $S_x$ and $S_y$ always constant
Energy-Based Models
- Assign lower energy to region near the data points
- Assign higher energy to energy outside of those data points (outliers)
- If there exists a function that can model the energy landscape, that function captured the dependencies between $x$ and $y$
.png)
Contrastive method
- Train the model so that it gives low energy to the data point with higher density and high energy to the two contrastive green dots
- Disadvantage:
- In high dimensional space, the number of contrastive points grows exponentially for the energy function to capture the right shape
.png)
Regularized method
- By introducing regularization, the energy function gives low energy to small volume of space
_(1).png)
Recommendations
- Instead of generative models, opt for joint-embedding architectures
- Instead of probabilistic model, opt for energy-based models
- Instead of contrastive methods, opt for regularized methods
- Instead of reinforcement learning, opt for model-predictive control
- Use RL only when planning doesn’t yield predicted outcome, to adjust the world model or the critic
Training a Joint-Embedding Predictive Architecture (JEPA) with Regularized Methods
- 4 terms in the cost function:
- Maximize information of $S_x$
- Maximize information of $S_y$
- Minimize information of latent variable $z$
- Minimize prediction error
- However, we it’s very hard to train with that cost function because we don’t have lower bound for those information
_(1).png)
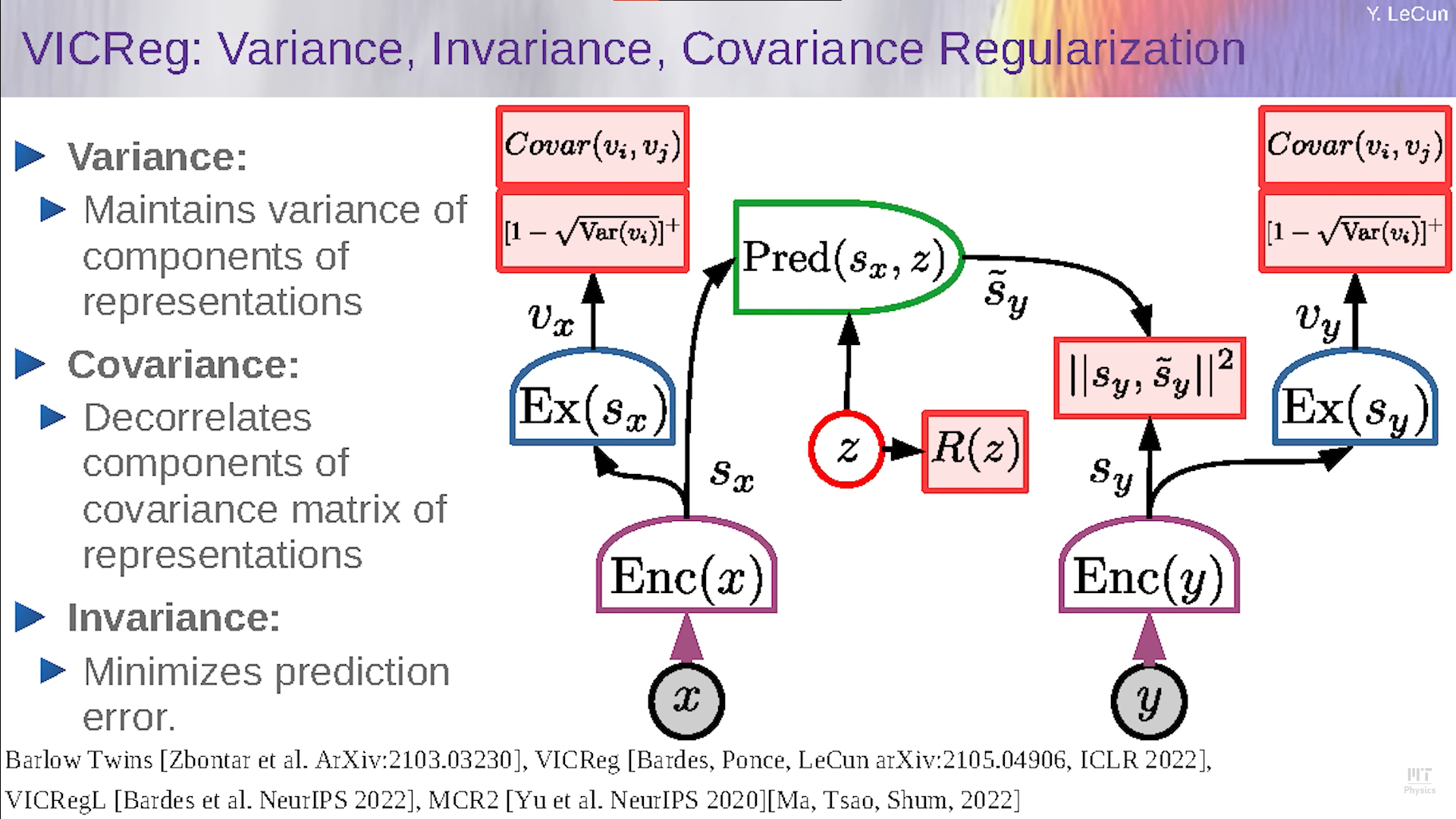
VICReg: Variance, Invariance, Covariance Regularization
To overcome the previous issue where we have no lower bound for the information content, we:
- Make sure the variance of every component of $S_x$ is at least one
- Make sure the components of $S_x$ are decorrelated
Problems to be solved

Conclusion
- We are still missing essential concepts to reach human-level AI
- Scaling up auto-regressive LLM will not take us there
- Learning World Models with SSL and JEPA
- Non-generative architecture, predicts in representation space
- Objective-driven AI Architectures
- Can plan their answers
- Must satisfy objectives: are steerable and controllable
- Guardrail objectives can make them safe
